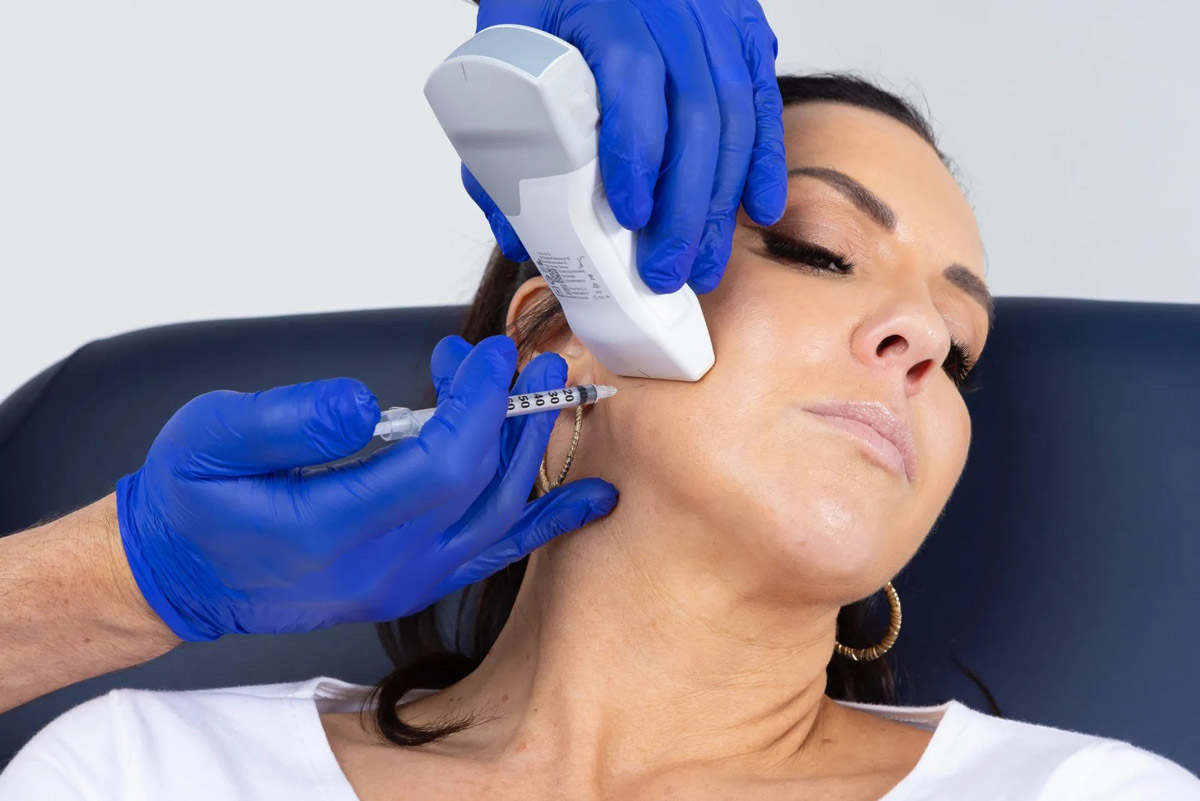


Chronic Migraines: Botox injections can be used as a preventive treatment for people who experience chronic migraines, defined as headaches that occur on 15 or more days per month. Botox can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines by blocking the release of certain chemicals involved in pain transmission.
Cervical Dystonia: Also known as spasmodic torticollis, cervical dystonia is a condition characterized by involuntary contractions of the neck muscles, causing the head to twist or turn in an abnormal position. Botox injections can help relax the affected muscles, reducing pain and improving range of motion.
Hemifacial Spasm: This condition involves involuntary contractions or twitching of the facial muscles on one side of the face. Botox injections can help reduce the frequency and severity of these spasms, improving quality of life for individuals with hemifacial spasm.